What is the blockchain and how does it works?
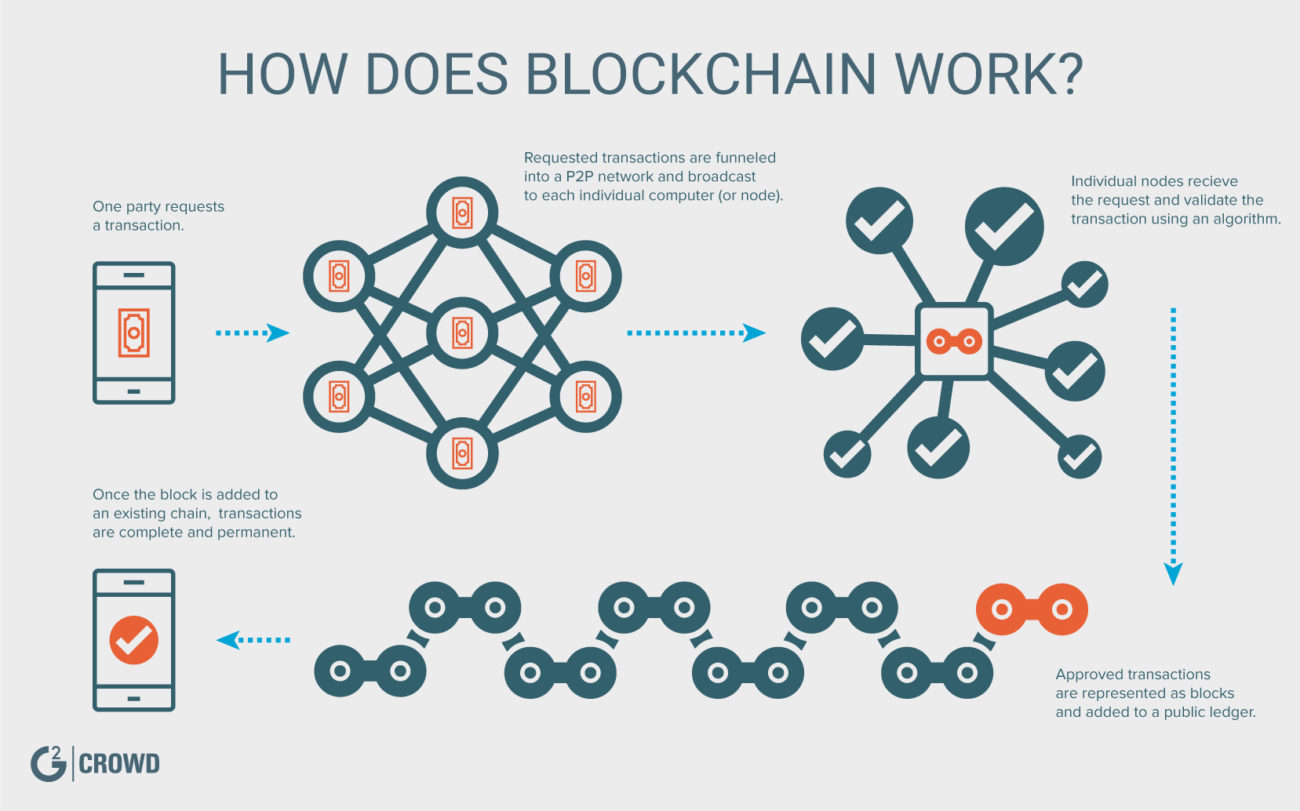
Image Source: https://media.g2crowd.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/23135723/blocks-2.jpg
The blockchain is an distributed digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value. blockchain technology created the backbone of IoT(Internet of Things). Blockchain was Originally devised for the digital currency, Bitcoin, the tech community is now finding other potential uses for the technology. The blockchain database isn’t stored in multiple locations, meaning the records it keeps are truly public and easily verifiable. The data is decentralized and this information doesn’t exist for a hacker to corrupt. The data is hosted by millions of computers simultaneously and its data is accessible to anyone on the internet. As data is stored across its network, it eliminates the risks that come with centralized system and provides identity for the users to access data using encryption technology. Each user’s identity has a public and private “key”. A “public key” (a long, randomly-generated string of numbers) is a user’s address in the block chain which can be shared with other users in the network. The “private key” is used to sign a signature and it is used to confirm that the transaction has come from the user.
Blockchain Types
The concept of the blockchain network cannot possibly serve all industries, different needs of businesses, and individual users. This has led to the creation of numerous blockchain networks, with different set of protocols, while the actual concept remains the same. Currently there are a number of blockchain networks available, the market has two types of block chains: permissionless (public) and permissions (private).
Permissionless blockchain systems and disadvantages
Permissionless blockchain networks contribute most of the market’s digital currencies. They allow every user to create a unique identity(public and private key) and begin interacting with the network, by submitting transactions, and hence adding entries to the ledger. Additionally, all organizations have the choice of running a node on the system. A conventional blockchain(Permissionless network), however, is not perfect. Concurrent processing of the same operations on multiple machines is not what you call efficient. A massive processing power is needed, a huge amount of effort and energy is consumed and yet the transactions are ridiculously slow. This leads to permissioned blockchain system.
Need for permissioned blockchain systems
Permissioned blockchains have evolved as an alternative to public blockchain to address the need for running blockchain technology among a set of known and identifiable participants that are required to be explicitly admitted to the blockchain network. The concept behind permissioned blockchain is that the participants require some means of identifying each other while not necessarily fully trusting each other.
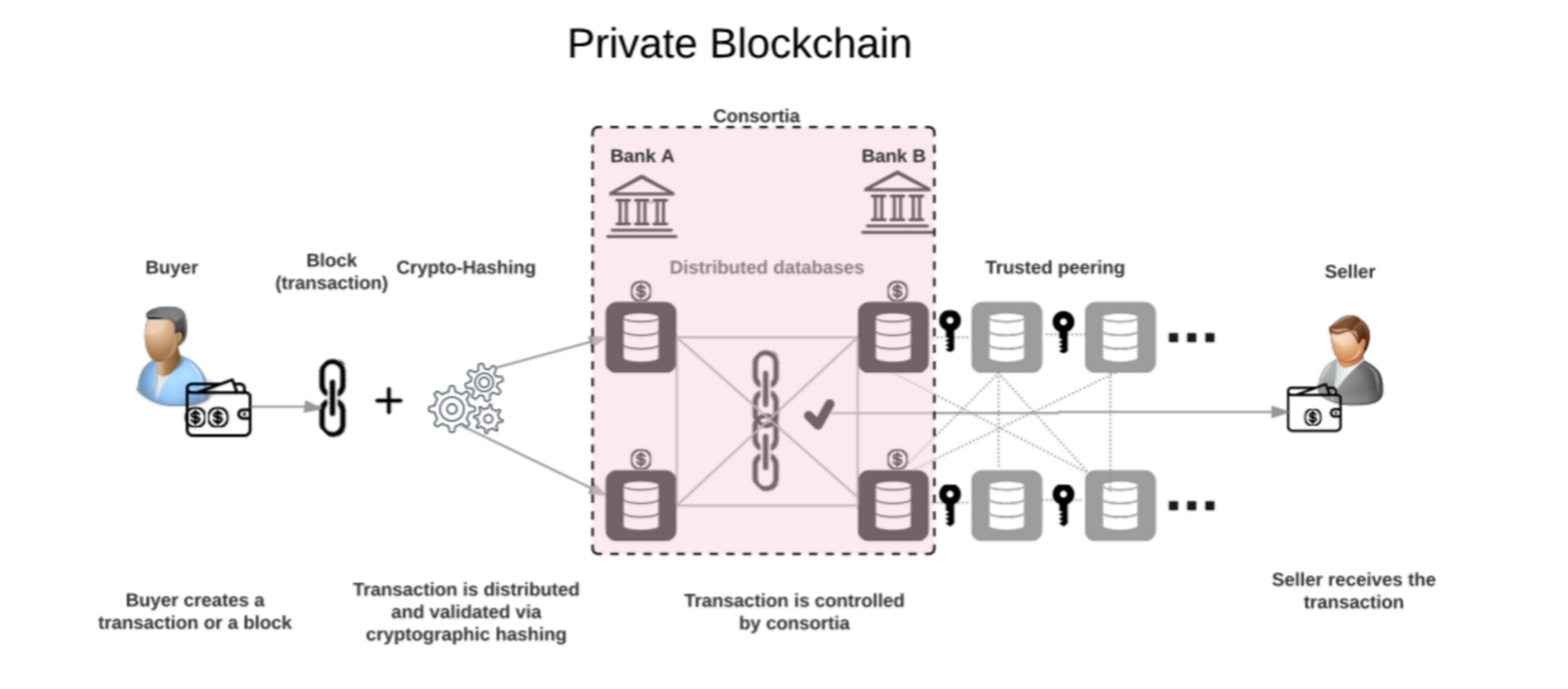
Image Source: https://www.devteam.space/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/private-blockchain.png
Permissioned network has a built in access-control layer built into blockchain nodes. All permission and profile maintenance will be taken care by this access-control network. So just like any other network, you have to register to the network before you can access it and the users can be assigned roles. These roles serve as the permission a user has on the network. For example, a role can be employee designated with a value “manager” or “team member”. These roles than determine what actions a user can perform. This is done by checking if that role has permission to execute that specific function. Such blockchains are famous among industry-level enterprises and businesses, for which security, identity and role definition are important. For instance, a manufacturer producing a product may use a permissioned blockchain which takes care of supply chain management. However, the transactions that occur on such a blockchain may also involve organization partners, banks, and other vendors involved in the supply and financing process. Though various parties involve in the network, don’t have to know the price at which the manufacturer supplies the products to various clients. Use of permissioned blockchains allows such role-limited implementations.
Transparency
The transparency depends upon how the business relationships are set up and how the blockchain is configured. Most permissioned blockchains do not have incentives built into them for performing consensus. The primary motive of permissioned blockchain participants is to minimize the cost, time, and ease of sharing information.
Privacy
Permissioned blockchains, such as Hyperledger Fabric, offer visibility into transaction details. For example, Imagine two suppliers, T1 and T2, doing business with a manufacturer, M. T1 might not want T2 to know the details of business with M — even though they are both members of the same blockchain network.
Scalability and Performance
Permissioned blockchains use consensus mechanisms that are inexpensive when compared to proof-of-work. Therefore, they enjoy better scalability and performance. Blockchains like Hyperledger Fabric offer additional features with respect to the roles of the nodes, including peers (that maintain state/ledger) and orderers (that consent on the order of transactions included in the ledger).
Practical Applications
Blockchain has already proven successful for a variety of tasks. The number of enterprises and even government organizations implementing smart contracts, distributed ledgers and other blockchain-based features are ever growing. Since it is in the development phase, we may not find use cases on the internet.




